Similarity Learning for Multiple Object Tracking
ABOUT THIS PROJECT
At a glance
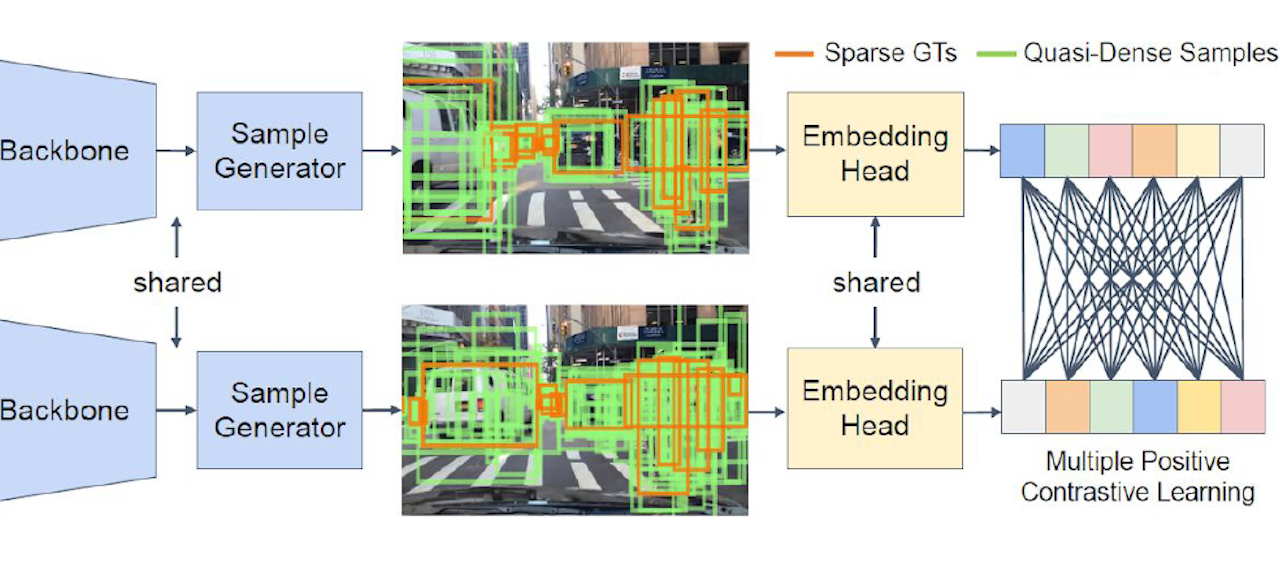
Similarity learning has been recognized as an crucial step for object tracking. However, existing multiple object tracking methods only use sparse ground truth matching as the training objective, while ignoring the majority of the informative regions on the images. In this project, we develop and extend Quasi-Dense Similarity Learning, which densely samples hundreds of region proposals on a pair of images for contrastive learning. We can naturally combine this similarity learning with existing detection methods to build Quasi-Dense Tracking (QDTrack) without turning to displacement regression or motion priors. We have found that the resulting distinctive feature space admits a simple nearest neighbor search at the inference time. Despite its simplicity, QDTrack outperforms all existing methods on MOT, BDD100K, Waymo, and TAO tracking benchmarks. It achieves 68.7 MOTA at 20.3 FPS on MOT17 without using external training data. Compared to methods with similar detectors, it boosts almost 10 points of MOTA and significantly decreases the number of ID switches on BDD100K and Waymo datasets.
| PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS | RESEARCHERS | THEMES |
|---|---|---|
| Trevor Darrell | Tracking, Autonomous Driving, Similarity Matching |

